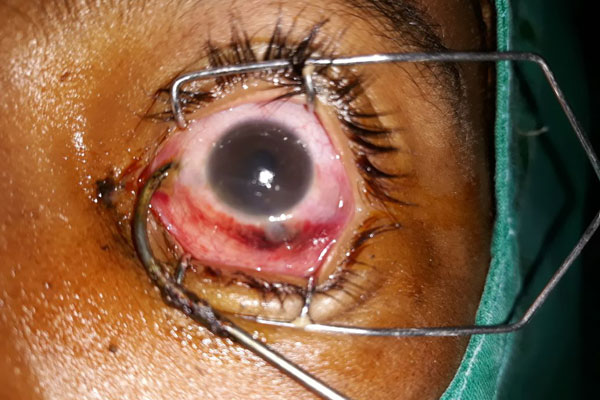
Fish hook injury to the eye and its management
Abstract
The most common cause of unilateral blindness in paediatric age groups, especially in developing countries, is ocular trauma. Trauma to the eye is very debilitating to the patient; hence, managing various types of penetrating and blunt injury to the eye provide a challenge to the ophthalmologist. It is simply preventable by the supervision
of the parents and caregivers. We will be discussing one such case and our experience in dealing with a fish hook injury to the eye in a 12-year-old boy—the challenges we faced and the precautions we took to give a good visual outcome.
References
Cao H, Li L, Zhang M, Li H. Epidemiology of pediatric ocular trauma in the Chaoshan Region, China, 2001–2010. PLoS One. 2013;8:e60844.
Agrawal R, Laude A, Taneja M. Fish hook injury of the eye. Int Ophthalmol. 2012;32(3):269-271.
Bartholomew RS, MacDonald M. Fish hook injuries of the eye. Br J Ophthalmol. 1980;64:531-533.
Jonas JB, Knorr HL, Budde WM. Prognostic factors in ocular injuries caused by intraocular or retrobulbar foreign bodies. Ophthalmology. 2000;107(5):823-828.
Aiello LP, Iwamoto M, Guyer DR. Penetrating and ocular fish hook injuries: surgical management and long-term visual outcome. Ophthalmology. 1992;99(6):862-866.
Ahmad SS, Seng CW, Ghani SA, Lee JF. Cut it out technique for ocular fish-hook injury. J Emerg Trauma Shock. 2013;6(4):293-295.
Copyright (c) 2020 Sangeetha Jeganathan, Suneetha Nithyanandam, Reji K. Thomas, Shubashree Karat

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors who publish with this journal agree to the following terms:
- Authors retain copyright and grant the journal right of first publication, with the work twelve (12) months after publication simultaneously licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License that allows others to share the work with an acknowledgement of the work's authorship and initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are able to enter into separate, additional contractual arrangements for the non-exclusive distribution of the journal's published version of the work (e.g., post it to an institutional repository or publish it in a book), with an acknowledgement of its initial publication in this journal.
- Authors are permitted and encouraged to post their work online (e.g., in institutional repositories or on their website) prior to and during the submission process, as it can lead to productive exchanges, as well as earlier and greater citation of published work (See The Effect of Open Access).


